CAREER DEVELOPMENT
In recent years, alcohol consumption patterns in the UK have undergone notable changes. According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), overall alcohol consumption has shown a gradual decline since its peak in the early 2000s. This shift can be attributed to a growing awareness of health issues associated with excessive drinking, changes in social norms, and the rise of alcohol-free alternatives.
Younger generations, in particular, are leading the way in moderation, with many choosing to reduce or entirely avoid alcohol. A growing trend of “mindful drinking” and an increase in the popularity of low-alcohol and non-alcoholic beverages cater to this demographic. The rise of health consciousness has encouraged many to seek alternative social options that do not revolve around drinking.
Despite these modern trends, alcohol remains deeply embedded in British culture. Pubs serve as social hubs, offering a space for communities to gather, relax, and engage with one another. Events like beer festivals and wine tastings celebrate local breweries and vineyards, fostering a sense of pride in regional produce.
Alcohol is also a focal point in many traditional celebrations, from weddings to national holidays. Drinks like gin, whisky, and cider have unique regional associations, with Scotland and Wales boasting their own traditional spirits.
The impact of alcohol on health and society has been a growing concern. The UK government has implemented measures aimed at reducing alcohol-related harm, including minimum unit pricing, health warnings on labels, and campaigns promoting responsible drinking. The National Health Service (NHS) continues to provide resources to help individuals understand the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption, including addiction, liver disease, and increased accident rates.
As of the latest statistics, cancer accounts for approximately 28% of all deaths in the UK, making it the leading cause of death. The most common types of cancer seen in the UK include breast, lung, prostate, and colorectal cancers. In 2020, it was estimated that there were over 390,000 new cases of cancer in the UK, a number that has continued to rise due to factors such as an aging population and lifestyle choices, particularly smoking, poor diet, and lack of physical activity.
Cancer is a multifaceted disease, and its development can be attributed to a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Tobacco use remains the most significant preventable cause of cancer, particularly lung cancer. Other risk factors include excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, exposure to certain chemicals, and prolonged sun exposure leading to skin cancers, such as melanoma.
Early detection is crucial in improving survival rates. The UK has implemented national screening programs for breast, cervical, and bowel cancer aimed at identifying these diseases in their early, most treatable stages. Advances in medical research have led to improvements in treatment modalities, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapies such as immunotherapy. Notably, the Cancer Drugs Fund in the UK plays a pivotal role in providing access to these innovative treatments for patients.
Healthcare Assistants in the UK are tasked with a wide array of responsibilities aimed at improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall patient experience. Their duties often include:
- Patient Care: Assisting patients with daily activities, such as personal hygiene, meal preparation, and mobility, ensuring comfort and dignity at all times.
- Monitoring Health: Observing patients’ conditions, including vital signs, and reporting any changes to the nursing team, which is crucial in preventing complications.
- Emotional Support: Providing companionship and emotional support, which helps in building trust and a positive rapport between patients and caregivers.
- Assisting in Procedures: Supporting registered nurses and doctors during medical procedures and treatments, thereby facilitating effective patient care.
While there is no formal certification for CNAs in the UK, prospective healthcare assistants typically undergo a mix of education and training. This may include:
- Formal Education: Many employers require potential HCAs to have a minimum of GCSEs in English and Mathematics. Further education, such as vocational qualifications (e.g., NVQ Level 2 in Health and Social Care), can be advantageous.
- Training Programs: In-house training provided by healthcare organizations equips candidates with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their roles effectively. This may cover areas such as infection control, manual handling, and basic life support.
- Experience: Practical experience in healthcare settings can be invaluable, and many enter the field through apprenticeship programs or as volunteers.
The significance of healthcare assistants cannot be understated. They provide essential support that allows registered nurses and other healthcare professionals to focus on complex medical care. By handling routine tasks and providing emotional support, HCAs help create a nurturing and healing environment for patients.
CBT began gaining traction in the UK during the late 20th century, primarily due to its empirical support and practical approach. The National Health Service (NHS) fully integrated CBT into its mental health services in the early 2000s, largely influenced by the findings of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), which endorsed CBT as an effective treatment for various mental health conditions. This shift towards evidence-based therapies marked a significant change in the UK's approach to mental health care.
In the UK, accessibility to CBT has improved significantly, largely due to the implementation of the Improving Access to Psychological Therapies (IAPT) program, which was launched in 2008. This initiative aimed to make talking therapies more widely available, with a specific focus on CBT as a frontline treatment. As a result, trained therapists are now available in various settings, including GP practices, community mental health services, and private sectors.
To ensure quality and consistency in treatment, various educational institutions offer rigorous training programs for mental health professionals. Accreditation from organizations such as the British Association for Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapies (BABCP) assures that practitioners meet established standards of competency.
Research indicates that CBT is effective in treating numerous psychological disorders. A multitude of studies have shown that it can lead to significant improvements in symptoms and functioning, with benefits that often extend beyond the duration of treatment. CBT is particularly praised for its structured, goal-oriented nature, allowing individuals to learn coping strategies they can apply throughout their lives.
Despite its widespread acceptance, there are challenges in the CBT landscape in the UK. Issues such as waiting times for therapy, variation in quality of service, and access in rural areas present ongoing concerns. Moreover, there is a need for continued research into the adaptation of CBT for diverse populations, including those with complex needs and cultural differences.
According to the latest data from the UK Office for National Statistics, approximately 1.2 million people are officially diagnosed with COPD in the UK, although it is estimated that a substantial number remain undiagnosed. COPD is the second leading cause of lung disease-related deaths in the country. The disease significantly impacts the quality of life, often leading to progressive disability and increased healthcare utilization due to frequent exacerbations.
The primary risk factor for COPD is smoking, accounting for approximately 80% of cases. While the smoking prevalence has declined over the years due to effective public health campaigns, the legacy of tobacco use continues to affect many older adults. Other risk factors include long-term exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollution, occupational dust and chemicals, as well as genetic factors such as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Patients with COPD typically present with symptoms such as chronic cough, sputum production, and progressive dyspnea (shortness of breath). Diagnosis is usually made through a combination of clinical evaluation, patient history, and spirometry—a non-invasive test that measures lung function. Early diagnosis is essential for effective management and can significantly slow disease progression.
Management of COPD in the UK focuses on reducing symptoms, improving quality of life, and minimizing exacerbations. This is achieved through a multifaceted approach that includes smoking cessation, pharmacological treatments (such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids), pulmonary rehabilitation, and, in some cases, surgery. Recent advancements in treatment options, including biologics and new inhalation therapies, are providing more tailored approaches to patient care.
In March 2020, the UK government implemented its first nationwide lockdown in a bid to contain the virus's spread. This involved closing schools, non-essential businesses, and limiting social gatherings. The lockdown measures were crucial in flattening the curve but also led to severe economic repercussions, with GDP dropping significantly and rising unemployment rates.
Throughout 2020 and 2021, vaccination efforts accelerated, with the UK becoming one of the first countries to approve a COVID-19 vaccine for emergency use. The rollout of vaccines, beginning in December 2020, was widely successful, with a large proportion of the adult population receiving their vaccinations by mid-2021. This led to a gradual easing of restrictions, allowing for a return to more normal life by summer 2021.
The emergence of new variants, including the Alpha variant, which was first identified in Kent, and Delta, which originated in India, posed additional challenges. These variants demonstrated increased transmissibility, leading to localized outbreaks and renewed concerns about hospitalizations and deaths despite the vaccination progress.
In late 2021 and early 2022, the Omicron variant emerged, causing a surge in cases but, importantly, appeared to result in milder illnesses among vaccinated individuals. This led to a reevaluation of strategies, and by early 2022, many restrictions were lifted, including mask mandates and the requirement for vaccine passports in certain venues.
As of 2023, the UK government has shifted its focus from emergency response to living with COVID-19 as an endemic virus. Vaccination programs continue, with updates for booster shots to deal with evolving variants, particularly for vulnerable populations.
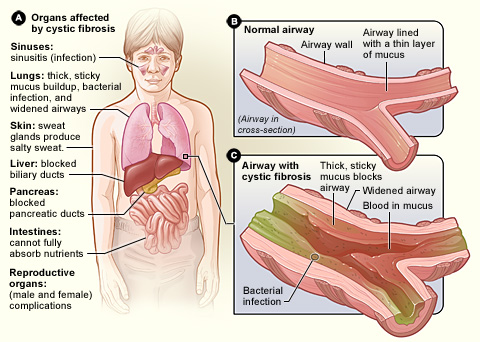
Cystic Fibrosis is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, which is responsible for producing a protein that regulates salt and water movement in and out of cells. The most common mutation in the UK is ΔF508, which affects the protein's function, leading to the production of thick, sticky mucus. This mucus can clog the airways, resulting in recurrent lung infections, inflammation, and progressive lung damage. In addition to respiratory issues, CF can also impede the function of the pancreas, leading to digestive difficulties and nutrient malabsorption.
Symptoms of CF can vary widely but often include persistent cough, difficulty breathing, frequent lung infections, poor growth, and difficulty gaining weight. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
In the UK, newborn screening for CF is standard practice, utilizing a blood test to measure levels of immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT). If results are abnormal, further diagnostic tests, including a sweat test and genetic screening, can confirm the diagnosis. Early detection has significantly improved outcomes, allowing for prompt treatment to manage symptoms and complications.
Over the past few decades, treatment for CF has evolved significantly. The care model in the UK emphasizes a multi-disciplinary approach, integrating specialists from respiratory medicine, nutrition, physiotherapy, and psychology to provide comprehensive care.
Recent advancements, particularly in drug therapies, have transformed the landscape of CF treatment. The introduction of CFTR modulators, such as ivacaftor and lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Orkambi), targets the underlying genetic defect, improving the function of the defective protein in a subset of patients. These therapies have shown considerable promise, leading to improved lung function and quality of life for many individuals with CF.
Despite the progress made, challenges remain. Access to the latest therapies can be uneven, and there are ongoing concerns about the long-term sustainability of treatment regimens. Additionally, the CF population is living longer, leading to new health concerns as individuals transition into adulthood.
One of the most well-established areas of electrophysiology in the UK is cardiac electrophysiology, which deals primarily with heart rhythm disorders. The National Health Service (NHS) has invested in advanced technologies and treatment options, including electrophysiology studies, ablation procedures, and implantable devices like pacemakers and defibrillators. Innovative procedures, such as catheter ablation, have become standard practices for managing conditions like atrial fibrillation, helping to reduce the risk of stroke and improve patients' quality of life.
Several UK's leading hospitals, such as the Royal Brompton Hospital in London and the Manchester Heart Centre, are at the forefront of cardiac electrophysiology. These institutions not only provide cutting-edge treatment options but also engage in research to develop new methodologies and devices that can enhance patient outcomes.
In addition to cardiac applications, the field of neurological electrophysiology is also gaining traction. With the rise in neurodegenerative diseases and conditions like epilepsy, electrophysiological techniques play an instrumental role in diagnosis and treatment. Techniques such as EEG (electroencephalogram) help clinicians understand brain activity and diagnose conditions more accurately. The UK is home to several leading research institutions, such as the University College London's Institute of Neurology, which fosters advancements in the understanding of brain electrical activity and its implications for various neurological conditions.
Research in electrophysiology is robust in the UK, with numerous universities and hospitals collaborating on clinical studies and trials aimed at improving existing treatments and exploring new therapeutic avenues. The UK also hosts various conferences and workshops that gather experts in the field, promoting knowledge sharing and collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and allied health professionals.
In the UK, becoming a gastroenterologist involves several years of rigorous training. After completing a medical degree, aspiring gastroenterologists undertake a foundation program, which typically lasts two years. Following this, they enter specialty training in internal medicine, usually spanning three years. This is followed by further training in gastroenterology, which generally lasts for an additional four years. Successful completion leads to the award of a Certificate of Completion of Training (CCT), permitting them to practice as consultants in the field.
Gastroenterologists often focus on specific sub-specialties, such as:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Managing conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Hepatology: Focusing on diseases of the liver, including hepatitis and cirrhosis.
- Endoscopy: Performing diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, such as colonoscopies and upper gastrointestinal endoscopies.
- Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Addressing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and dyspepsia.
Their expertise is instrumental in the early diagnosis of serious conditions, including gastrointestinal cancers, which underscores the importance of routine screenings and specialist consultations.
Gastroenterologists are responsible for conducting a variety of diagnostic tests, including blood tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic procedures. They provide tailored treatment plans that may involve medications, lifestyle modifications, or surgical interventions in collaboration with surgeons and other healthcare professionals.
In recent years, the increasing prevalence of gastrointestinal diseases, partly due to lifestyle choices, has elevated the need for gastroenterological services. Conditions such as obesity, fatty liver disease, and gastrointestinal cancers are on the rise, placing additional strain on healthcare resources and highlighting the importance of early intervention and public awareness.
Immunocytochemistry operates on the principle of using antibodies that specifically bind to target antigens in cells spun onto slides. After fixation and permeabilization of the cells to allow antibodies to penetrate, the samples are treated with labeled antibodies. These antibodies are often conjugated to fluorescent or chromogenic agents, which allow for visualization under a fluorescence microscope or a light microscope, respectively. This specificity helps in determining the presence, location, and quantity of proteins of interest in cellular contexts.
In the UK, ICC is widely utilized in pathology laboratories for both diagnostic and prognostic purposes. It is particularly significant in oncology for the classification of tumors and the determination of appropriate treatment protocols. For instance, breast cancer diagnosis often involves ICC to assess hormone receptors (such as estrogen and progesterone receptors) which guide therapy decisions.
Furthermore, ICC is pivotal in microbiology for identifying pathogenic organisms within clinical specimens, thus aiding in precise diagnoses and appropriate treatment strategies.
The UK boasts a robust research community that employs ICC in various studies, from basic research seeking to understand cellular mechanisms to translational research aiming to apply findings in clinical settings. Institutions such as universities and biomedical research centres contribute to advancements in ICC methodologies, improving sensitivity and specificity while expanding the range of detectable antigens.
To ensure high standards in ICC practice, the UK has established comprehensive training programs for pathologists and laboratory technicians. The Royal College of Pathologists and other professional bodies provide guidelines and resources to maintain accreditation and proficiency in immunocytochemical techniques.
Regulatory bodies, including the UK Health Security Agency and the Care Quality Commission, oversee laboratory practices to ensure safety, quality, and ethical compliance in immunocytochemistry.
Crohn's Disease: This form can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It often penetrates deeper into the intestinal walls, which can lead to complications such as strictures, abscesses, and fistulas.
Ulcerative Colitis: Typically confined to the colon and rectum, ulcerative colitis causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers in the inner lining of the large intestine. It presents in varying degrees of severity and can lead to significant health complications.
Common symptoms of IBD include abdominal pain, diarrhea (often bloody), fatigue, unintended weight loss, and malnutrition. The onset of symptoms can be gradual or sudden, often leading to periods of remission and flare-up.
Diagnosis usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, such as colonoscopy or MRI scans. Early diagnosis is crucial in managing IBD effectively to minimize complications and improve quality of life.
Living with IBD can significantly impact daily life, including work, social activities, and mental health. Patients often face challenges related to managing symptoms, and many report feelings of isolation or anxiety due to the unpredictable nature of the disease. Moreover, the stigma surrounding bowel diseases can prolong suffering and delay seeking help.
While there is currently no cure for IBD, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and reduce inflammation. These include:
-
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and control immune responses.
-
Diet and Nutrition: Specialized diets may help manage symptoms and ensure adequate nutrition, especially during flare-ups.
-
Surgery: In severe cases, surgical interventions may be required to remove damaged sections of the gastrointestinal tract, particularly for Crohn's disease.
ILDs encompass over 200 different conditions that primarily affect the interstitial space of the lungs, which is the tissue and space around the air sacs. Common types include idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, pneumoconiosis (often related to occupational exposures), and connective tissue disease-related lung disease. Symptoms typically include persistent dry cough, shortness of breath on exertion, and fatigue. The exact cause of many ILDs remains unclear, but factors such as environmental exposures, autoimmune diseases, and genetic predisposition play a role.
In the UK, the prevalence of ILD is rising, in part due to an aging population and improved diagnostic techniques. It is estimated that around 5-10 people per 100,000 suffer from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis alone. Other forms of ILD are often underdiagnosed, as symptoms can mimic other respiratory conditions.
Diagnosis of ILD typically involves a comprehensive approach, including a detailed patient history, physical examination, pulmonary function tests (PFTs), imaging studies (such as high-resolution computed tomography scans), and sometimes lung biopsies. The multidisciplinary approach is crucial due to the variety of conditions under the ILD umbrella. Specialist centers in the UK are increasingly collaborating across disciplines to improve diagnosis and patient care.
Though there is no cure for most ILDs, management focuses on slowing disease progression and maintaining quality of life. Treatment options may include:
-
Medications: Anti-fibrotic drugs like pirfenidone and nintedanib have been shown to slow the progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs are also utilized for autoimmune-related ILDs.
-
Oxygen Therapy: Supplementing oxygen can help alleviate respiratory symptoms and improve the quality of life in patients experiencing significant hypoxemia.
-
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Tailored physical therapy can enhance functional capacity, endurance, and overall well-being.
-
Lung Transplantation: In severe cases, lung transplantation may be the only option, especially for younger patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Interventional Radiology involves the use of imaging technologies such as X-rays, ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI to perform minimally invasive treatments. Through small incisions, interventional radiologists can access the vascular and non-vascular structures of the body, allowing them to conduct procedures ranging from biopsies and drain placements to more complex interventions like angioplasty and stent placements.
In the UK, interventional radiologists play a crucial role in managing various medical conditions, including:
-
Vascular Diseases: IR is extensively used in treating conditions like peripheral artery disease, varicose veins, and vascular malformations.
-
Oncology: Interventional radiologists undertake procedures such as tumor ablation and chemoembolization to target and destroy cancerous cells while preserving healthy tissue.
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders: They perform procedures like biliary drainage and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) to manage conditions affecting the liver and biliary tract.
-
Pain Management: Familiar techniques include vertebroplasty and radiofrequency ablation, which help alleviate chronic pain through targeted interventions.
One of the primary benefits of IR is its minimally invasive nature, which often leads to shorter recovery times, reduced hospital stays, and lower rates of complications compared to traditional surgical methods. Patients typically experience less pain and scarring, enabling quicker return to normal activities. Additionally, many interventional radiology procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, further enhancing patient convenience.
The UK has seen an increase in the number of interventional radiologists and specialized training programs, providing healthcare professionals with the skills necessary to excel in this growing field. The NHS, along with private healthcare providers, has recognized the value of IR, integrating its practice into various treatment pathways to optimize patient outcomes.
Professional organizations like the Royal College of Radiologists (RCR) and the British Society of Interventional Radiology (BSIR) are pivotal in guiding best practices, advancing research, and facilitating continuous education within the field. These institutions also emphasize the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration, ensuring that patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their specific needs.
Despite its advancements, Interventional Radiology in the UK faces challenges, including limited resources, accessibility issues, and the need for increased public awareness about the benefits of these treatments. Continued investment in training, research, and technology is vital for the specialty's future growth.
In the UK, the process for lung transplantation involves several key steps, starting with thorough evaluations at specialized transplant centers. The NHS Blood and Transplant (NHSBT) organization oversees organ donation and transplantation. Patients undergo rigorous assessments to determine their suitability for a transplant, which include medical and psychological evaluations.
Eligible patients are placed on a waiting list, where they are matched with suitable donor lungs based on blood type, size, and medical urgency. The waiting time can vary significantly, often extending from a few months to several years, depending on the availability of suitable donors.
Organ donation in the UK operates under an opt-out system, implemented in 2020, where all adults are presumed to be donors unless they explicitly state otherwise. This move aims to increase the number of available organs and has shown promise in increasing transplantation rates. Public awareness campaigns have also played a crucial role in promoting the importance of organ donation to save lives.
As of the latest data, around 180 lung transplants are performed annually in the UK. Despite advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, challenges still exist, primarily around the organ shortage and the need for a broader donor base. The success rates for lung transplants have improved over the years, with approximately 80% of recipients surviving one year post-transplant and around 50% surviving five years.
Mechanical ventilation is a life-sustaining intervention that provides respiratory support to patients who are unable to breathe adequately on their own. This can be due to various conditions, including acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations, pneumonia, and following major surgeries. In the UK, healthcare providers utilize both invasive (endotracheal intubation) and non-invasive ventilation techniques (NIV) to enhance oxygenation and carbon dioxide removal, tailoring the approach to each patient's unique needs.
The landscape of mechanical ventilation has been revolutionized in the UK through the development of sophisticated ventilators that offer a range of modes and settings, allowing clinicians to customize treatment strategies effectively. Modern ventilators incorporate advanced monitoring capabilities that provide real-time feedback on a patient’s respiratory status, enabling prompt adjustments to ensure optimal lung protection while minimizing potential complications.
In the UK, guidelines from organizations such as the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and the British Thoracic Society (BTS) have been established to support clinicians in delivering safe and effective mechanical ventilation. These guidelines emphasize the importance of evidence-based practices, including lung-protective ventilation strategies, which aim to reduce ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and improve patient outcomes.
Proper training and education for healthcare professionals are essential for the effective use of mechanical ventilation. In the UK, medical education programs and specialized training courses ensure that doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists are well-equipped to manage ventilated patients. Simulation-based education has become increasingly popular, allowing healthcare providers to practice their skills in a controlled environment and develop the confidence needed for critical care situations.
Despite its benefits, the application of mechanical ventilation presents several challenges, including ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), patient-ventilator dysynchrony, and the need for prolonged sedation. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted both the importance and strain on mechanical ventilation resources within the NHS, leading to a reevaluation of protocols and approaches to care.
According to the Mental Health Foundation, one in four people in the UK will experience a mental health problem in their lives. Common issues include anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Recent surveys and studies indicate that mental health issues have been exacerbated by the pandemic, with reports showing significant increases in anxiety and depression rates with the onset of lockdowns and social isolation.
Despite the increasing recognition of mental health’s importance, access to mental health services remains uneven. The National Health Service (NHS) is the primary provider of mental health care in the UK, but it faces significant challenges. Long waiting times for treatment, particularly for counselling and psychotherapy, can lead to patients feeling abandoned and hopeless. The NHS has outlined plans to increase mental health funding, which is encouraging, yet there are calls for a more robust and consistent approach to mental health care.
The UK government has implemented several initiatives aimed at addressing mental health challenges. The "Mental Health Act 1983" has been undergoing reform, acknowledging the need for modernized approaches to mental health that prioritize patient rights. Additionally, the “Five Year Forward View for Mental Health” strategy aims to improve access to services and integrate mental health care into physical health care settings, providing a more holistic approach to patient health.
Statistics indicate that around 130,000 people in the UK are living with MS, making it one of the highest prevalence rates in the world. While the specific causes of MS remain uncertain, it is thought to be an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective myelin sheath surrounding nerve fibers. The condition is more commonly diagnosed in women than men, with a ratio of approximately 3:1.
The onset of MS typically occurs between the ages of 20 and 40, but it can develop at any age. The geographical distribution of MS shows that it is more prevalent in northern latitudes, leading researchers to explore environmental and genetic factors that may contribute to this trend.
There are several forms of MS, including:
-
Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS): The most common form, characterized by unpredictable flare-ups (relapses) followed by periods of recovery (remissions).
-
Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS): Initially begins as RRMS but eventually transitions into a progressive stage, compounded by a gradual decline in function.
-
Primary Progressive MS (PPMS): A less common form that leads to a gradual worsening of symptoms from the onset without distinct relapses.
-
Progressive-Relapsing MS (PRMS): A rare form that combines progressive disease with occasional relapses.
Symptoms of MS can be varied and unpredictable, including fatigue, mobility issues, numbness, vision problems, and cognitive changes. The diverse nature of the disease means that each individual’s experience can differ widely.
The management of MS in the UK encompasses a multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and MS specialists. Treatment options include disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of relapses and symptomatic treatments to manage individual symptoms. Access to these treatments can vary across regions, as healthcare is devolved across England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland.
In addition to clinical management, support networks play a vital role in the lives of those with MS. Organizations such as the MS Society and other local charities provide resources, community, and advocacy for patients. They focus on raising awareness, funding research, and supporting individuals and families living with MS.
There are several types of muscular dystrophy, with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) being the most common form diagnosed in children. DMD typically manifests between the ages of 2 and 6, primarily affecting boys, leading to significant muscle degeneration and loss of mobility over time. Other forms, such as Becker Muscular Dystrophy, Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy, and Myotonic Dystrophy, exhibit a range of symptoms and age of onset.
Diagnosis of muscular dystrophy often involves a combination of physical examinations, genetic testing, and muscle biopsy to determine the specific type of MD present. Early diagnosis is crucial, as it can lead to proactive interventions that may enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
While there is currently no cure for muscular dystrophy, treatment strategies aim to slow the progression of the disease and alleviate symptoms. In the UK, multidisciplinary care teams—including physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and neurologists—work collaboratively to provide tailored care. Treatments may include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, physical therapies to improve mobility, and assistive devices to aid independence.
Various organizations in the UK, such as Muscular Dystrophy UK and the Duchenne Family Support Group, provide invaluable resources, advocacy, and support for patients and their families. These organizations focus on promoting research to find effective treatments and improve care standards, while also raising awareness to build a supportive community.
In the UK, cardiovascular diseases, including myocardial infarction, are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. According to the British Heart Foundation, around 100,000 people experience a heart attack each year. Despite advancements in medical treatment and emergency care, the incidence of MI remains high, particularly among older adults and individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
Myocardial infarction primarily results from coronary artery disease (CAD), where the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to atherosclerosis—a buildup of fatty deposits. Several risk factors contribute to the development of CAD and subsequent myocardial infarction, including:
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, physical inactivity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption significantly increase the risk of heart disease.
- Comorbid Conditions: High blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels are major risk factors for MI.
- Genetics: A family history of heart disease can elevate an individual's risk.
Recognizing the symptoms of a myocardial infarction is critical for timely intervention. Common signs include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (often described as a feeling of pressure, squeezing, or fullness)
- Radiating pain in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating, nausea, or lightheadedness
In women, symptoms can sometimes differ, presenting more frequently as fatigue, anxiety, and abdominal discomfort rather than classic chest pain.
The NHS is structured primarily through four distinct bodies for each of the UK's constituent countries: NHS England, NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care in Northern Ireland. Each body operates independently within its framework but shares the common ethos of providing comprehensive health services.
Funding for the NHS primarily comes from taxation, with a significant contribution from general taxation and National Insurance contributions. This model allows the NHS to operate without direct charges for most services, distinguishing it from healthcare systems in many other countries, where insurance or co-pays are often necessary.
The NHS provides a broad range of services, including general practice, emergency care, hospital services, mental health services, and long-term care. General practitioners (GPs) act as the first point of contact for patients, playing a crucial role in the referral process to specialist services. Furthermore, the NHS is also responsible for public health initiatives, such as vaccination programs and health education, which are instrumental in promoting overall community health.
Despite its successes, the NHS faces numerous challenges, including funding constraints, an aging population, increased demand for services, and workforce shortages. These pressures have led to ongoing debates about reform and innovation within the system. Digital transformation has been a pivotal focus, with efforts to integrate technology into healthcare delivery. Initiatives such as telemedicine and electronic health records have gained prominence, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated the adoption of remote consultations and other digital health services.
Nuclear medicine in the UK gained prominence in the mid-20th century. With advancements in technology and an increasing understanding of biological processes at the molecular level, it has evolved significantly. The establishment of specialized centers and the development of radiopharmaceuticals have further enhanced its application in clinical practice.
Nuclear medicine encompasses a range of procedures, including:
-
Diagnostic Imaging: Techniques such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) enable clinicians to visualize and quantify biological functions in real time. This is particularly valuable for detecting cancers, evaluating heart function, and assessing neurological disorders like Alzheimer's disease.
-
Therapeutic Applications: Radioiodine therapy for thyroid disorders and targeted radiotherapy for certain cancers represent some of the therapeutic roles nuclear medicine plays. These treatments often provide effective alternatives when conventional therapies may not be suitable.
-
Research and Development: The UK is home to several leading research institutions and universities that focus on the development of novel radiopharmaceuticals and innovative imaging techniques. Collaborative research initiatives also promote advancements in this field.
The practice of nuclear medicine in the UK is tightly regulated to ensure patient safety and the ethical use of radioactive materials. The Care Quality Commission (CQC) oversees the quality and safety of healthcare services, while the Department of Health and Social Care provides guidelines on the use of ionizing radiation in medical procedures. Hospitals and clinics adhere to strict protocols to minimize radiation exposure to patients and staff.
Nuclear medicine is integrated into the broader framework of the National Health Service (NHS). Nuclear medicine departments often work closely with other specialties, fostering a multidisciplinary approach to patient care. This integration is essential for delivering comprehensive diagnostic insights and personalized treatment plans.
In PD, a sterile dialysis solution is introduced into the abdominal cavity through a catheter implanted in the belly. The peritoneum, which is the lining of the abdominal cavity, acts as a semi-permeable membrane, allowing waste products and excess fluids to move from the blood into the dialysis solution. After a prescribed dwell time, the solution, now containing waste materials, is drained out and replaced with fresh solution. The process can be done manually several times a day (Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis - CAPD) or through a machine that automates the exchange cycle at night (Automated Peritoneal Dialysis - APD).
One of the significant advantages of PD is its flexibility and convenience. Patients can manage their treatment at home, allowing for a lifestyle that is less restrictive compared to in-center hemodialysis. Additionally, PD is especially beneficial for patients who wish to maintain a degree of independence from healthcare facilities. Studies have shown that PD can be as effective as hemodialysis in maintaining quality of life and patient survival, depending on individual circumstances.
In the UK, PD is included in the National Health Service (NHS) renal care services, promoting its use as a first-line dialysis option where appropriate. The UK Renal Registry monitors and reports on the use of dialysis modalities, indicating a steady adoption of PD, particularly among patients seeking home-based therapies.
However, challenges exist regarding patient education and training, as successful PD requires a commitment to learning the technique and effectively managing one's own care. Healthcare professionals, including nephrologists and specialized nurses, play a crucial role in providing patients with the information and support needed to initiate PD.
As part of a broader initiative to enhance kidney care, the NHS is exploring ways to increase the uptake of home dialysis options, including PD. The Renal Quality Improvement Programme (RQIP) encourages healthcare providers to optimize patient pathways and promote the benefits of home therapies.
In the UK, pneumonia is one of the leading causes of hospital admissions and is particularly impactful among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, very young children, and those with pre-existing health conditions. According to Public Health England, there are approximately 250,000 cases of pneumonia each year, resulting in around 40,000 hospital admissions and thousands of deaths annually.
Bacterial pneumonia, most commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, is frequently linked to serious complications if not promptly treated. Viral pneumonia, often resulting from influenza or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), has become more prevalent, especially during seasonal outbreaks. Risk factors include smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), diabetes, and a weakened immune system, all of which exacerbate the likelihood of developing pneumonia.
Common symptoms of pneumonia include cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing, fatigue, and fever. Early diagnosis is crucial, as it can lead to timely intervention. Healthcare providers typically rely on physical examinations, imaging tests such as chest X-rays, and laboratory tests (such as blood cultures) to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for pneumonia varies based on its cause and severity. Bacterial pneumonia is usually treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications. For patients with underlying health issues or severe symptoms, hospitalization may be necessary for more intensive care, including oxygen therapy or intravenous antibiotics.
TBI affects a diverse range of age groups, but certain demographics are at higher risk. Data from the Brain Injury Association indicates that men aged 15 to 24 and older adults over 75 are particularly vulnerable. The National Health Service (NHS) reports that approximately 1.4 million people attend Accident & Emergency departments annually with head injuries, with a significant portion diagnosed with a concussion or TBI.
The societal impact of TBI is profound. Beyond the immediate medical care required, individuals may experience long-term health complications, affecting their ability to work, engage in social activities, and maintain relationships. The financial burden associated with TBI, encompassing healthcare costs, rehabilitation, and lost productivity, is substantial, with estimates suggesting billions of pounds are spent each year in the UK on related services.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in TBI patients. In the UK, emergency departments utilize a variety of clinical assessments and imaging techniques to diagnose the severity of the injury. Treatment protocols often involve both immediate medical care and long-term rehabilitation programs tailored to the individual's needs. Multidisciplinary teams—including neurologists, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and psychologists—play a vital role in the recovery process.
Post-injury rehabilitation is essential for helping individuals regain independence and improve their quality of life. Various support services are available throughout the UK, ranging from specialized rehabilitation centres to community-based programs. Advocacy groups, such as Headway and the Brain Injury Association, provide resources, guidance, and emotional support for individuals and families navigating the complexities of recovery.
The UK's National Health Service (NHS) has embraced whole genome sequencing as part of its genomic medicine initiative. The Genomic Medicine Service (GMS), launched in 2021, aims to integrate genomic information into clinical practice, offering WGS as a diagnostic tool for conditions such as rare genetic diseases and certain cancers. This service is designed to facilitate early detection and treatment, improving patient outcomes and reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
Furthermore, WGS has played a crucial role in public health surveillance, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. The UK became a global leader in genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2, with the COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium (COG-UK) spearheading efforts to monitor variants of the virus. This rapid genomic analysis has been instrumental in informing public health responses and understanding the evolution of the virus, helping to guide vaccination strategies and containment measures.
The United Kingdom is home to some of the world’s leading genomics research institutions, such as the Wellcome Sanger Institute and the UK Biobank. These organizations have harnessed WGS to uncover insights into genetic predispositions for various diseases, advancing our understanding of complex health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and mental health disorders.
Moreover, large-scale projects, such as the 100,000 Genomes Project, have collected and sequenced genomes from diverse populations across the UK, contributing to a vast database that drives genomic research forward. This wealth of genomic data is paving the way for new discoveries in disease mechanisms, treatment responses, and drug development.
WGS holds significant promise for personalized medicine, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatments to individuals based on their genetic makeup. In the UK, initiatives such as the NHS Genomic Medicine Service are moving towards integrating genomic data into routine care, enabling clinicians to make informed decisions regarding treatment options and disease management. This approach not only improves patient care but also enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery.